6 Pin Connector Enables Versatile Device Interfaces
The requirement for reliable, multi-pathway electrical interfaces spans diverse industries, from consumer electronics to industrial automation and automotive systems. Meeting this need, the 6 Pin Connector has become a standardized and widely adopted solution, offering a balanced number of contacts for transmitting combinations of power, ground, data, and control signals within a single compact unit. Its six discrete circuits provide greater functional capability than simpler connectors, enabling it to support more complex devices and subsystems. The prevalence of the 6 Pin Connector underscores its role as a versatile workhorse in product design, facilitating everything from peripheral device connections and sensor interfacing to internal module communication.
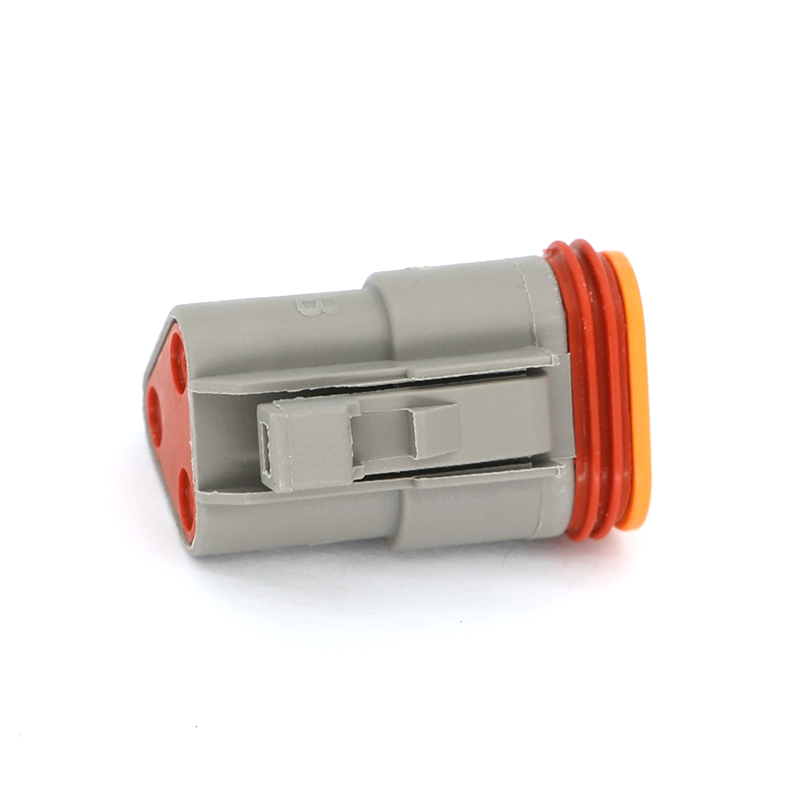
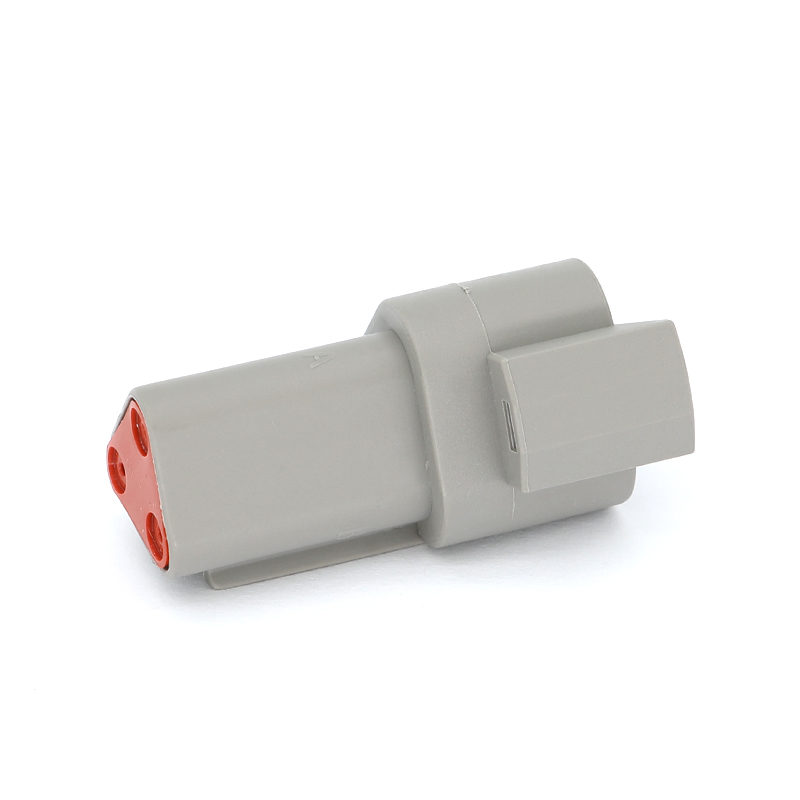
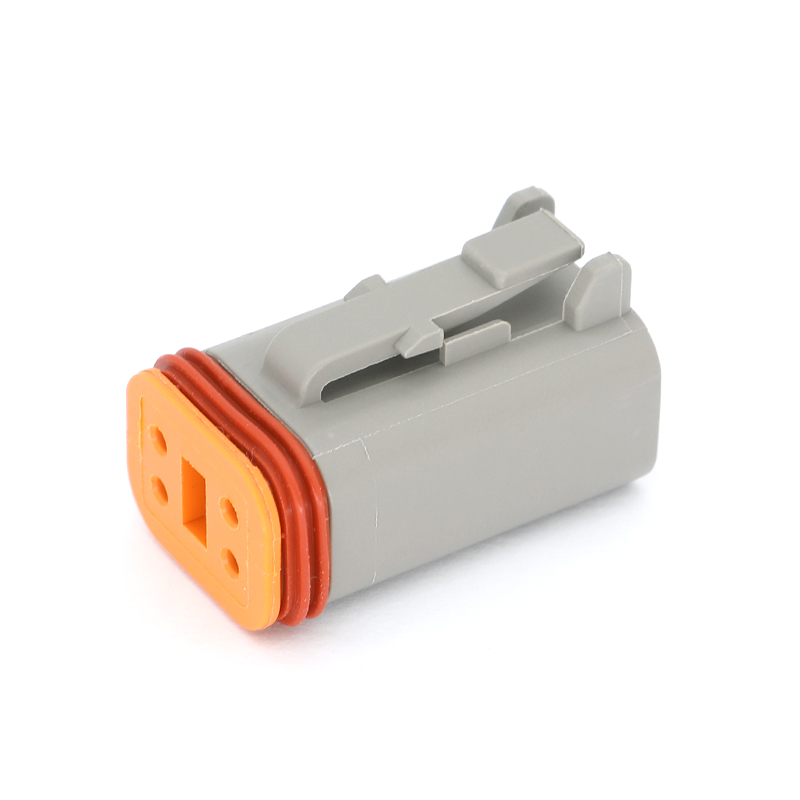
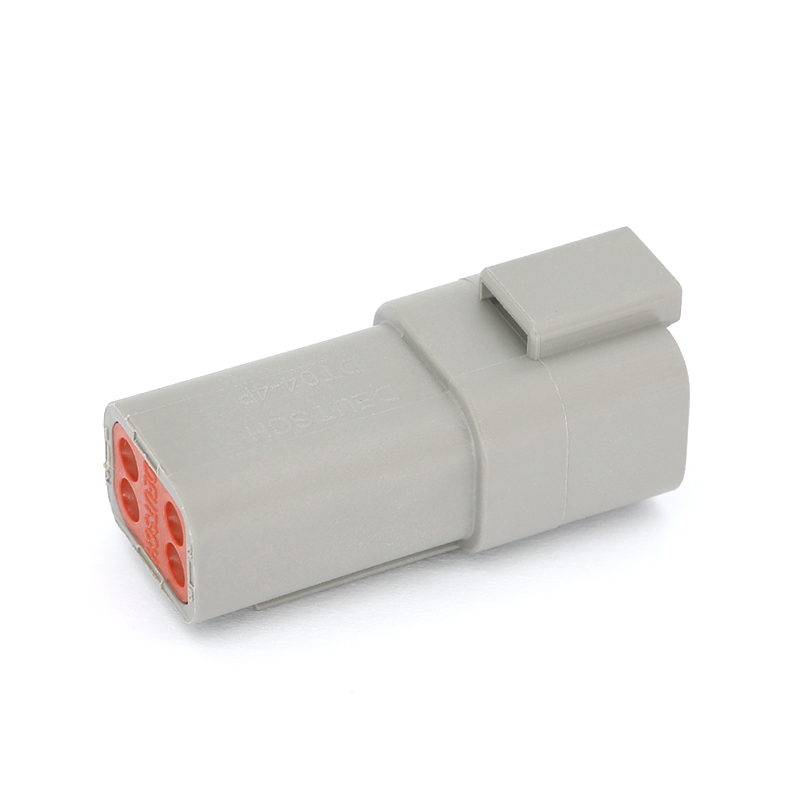
The physical and electrical design of a 6 Pin Connector is tailored to ensure performance and durability in its intended application. The connector housing is typically constructed from engineering-grade plastics or, in some industrial applications, metal, providing structural integrity and protection for the internal pins. A secure mating mechanism—such as screws, latches, or a friction-fit design with alignment keys—is crucial to prevent accidental disconnection due to vibration or cable strain. The six contact pins, often arranged in a single or double row, are commonly made from machined or stamped brass, phosphor bronze, or other conductive alloys, with plating options like gold over nickel for predominant corrosion resistance and stable contact in low-voltage signal applications. This construction ensures that each pin maintains a reliable electrical path capable of handling its designated current and signal integrity requirements.
The application spectrum for the 6 Pin Connector is remarkably broad. In computing and consumer electronics, a 6 Pin Connector is famously used as a supplementary power input for graphics processing units (GPUs) and other high-performance components, delivering dedicated power beyond what the motherboard slot can supply. In audio-visual equipment, it can be found in professional audio interfaces and certain video control systems. Within industrial settings, 6 Pin Connector variants are employed for connecting sensors, solenoids, and small motor drives on automated machinery, where they consolidate power and control signals. The automotive industry utilizes sealed 6 Pin Connector types for connections in lighting clusters, certain control modules, or trailer wiring harnesses, where multiple functions like tail lights, brake lights, turn signals, and electric brakes need to be managed.
Current technological trends are pushing the 6 Pin Connector to evolve in terms of performance density and environmental resilience. The ongoing miniaturization of electronics creates demand for smaller-pitch 6 Pin Connector designs that offer the same pin count in a reduced footprint. The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and edge devices necessitates connectors that are robust enough for field deployment, often requiring versions with IP-rated sealing against dust and moisture.
The 6 Pin Connector is expected to maintain its relevance by adapting to emerging standards and material innovations. We may see wider adoption of connectors using Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) housings for better performance in reflow soldering processes, and the integration of locking and coding features that prevent mis-mating in complex assemblies. Its role in power delivery, particularly for portable devices and distributed low-voltage systems, may be redefined with new fast-charging standards. As a fundamental interconnect component, the 6 Pin Connector exemplifies the principle of standardized modularity, providing designers with a reliable, off-the-shelf solution to create sophisticated electrical interfaces.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى 简体中文
简体中文